Table of Contents
Introduction
How Has API Management Evolved?
Phase 1: Manual API Management
Phase 2: Automated API Management
Phase 3: Autonomous API Management
Why Should You Automate API Management?
1. Scale
2. Speed
3. Cost
4. Risk Mitigation
How to Transition from Manual API Management?
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment (Months 0-3)
Phase 2: Automation Foundation (Months 4-6)
Phase 3: Intelligence and Autonomy (Months 7-12+)
Things to Consider Before Transitioning to Autonomous API Management
The Path Forward
Introduction
APIs now drive over 60% of internet traffic, yet most organizations still manage them manually, creating critical competitive disadvantages. They struggle with spreadsheet-based inventories and email approvals, while early movers—those deploying autonomous API management systems that self-heal, predict demand, and optimize performance without human intervention—enjoy greater efficiency and market positioning.
These leaders are achieving 50% faster incident resolution and real-time market responsiveness that reactive competitors cannot match. Consequently, the question facing executives isn’t whether API automation matters, but how quickly they can transition from manual processes to autonomous API management.
Read on to see how autonomous management presents a strategic imperative that determines market positioning for organizations today. We also discuss how you can automate your API operations via a three-step implementation guide.
How Has API Management Evolved?
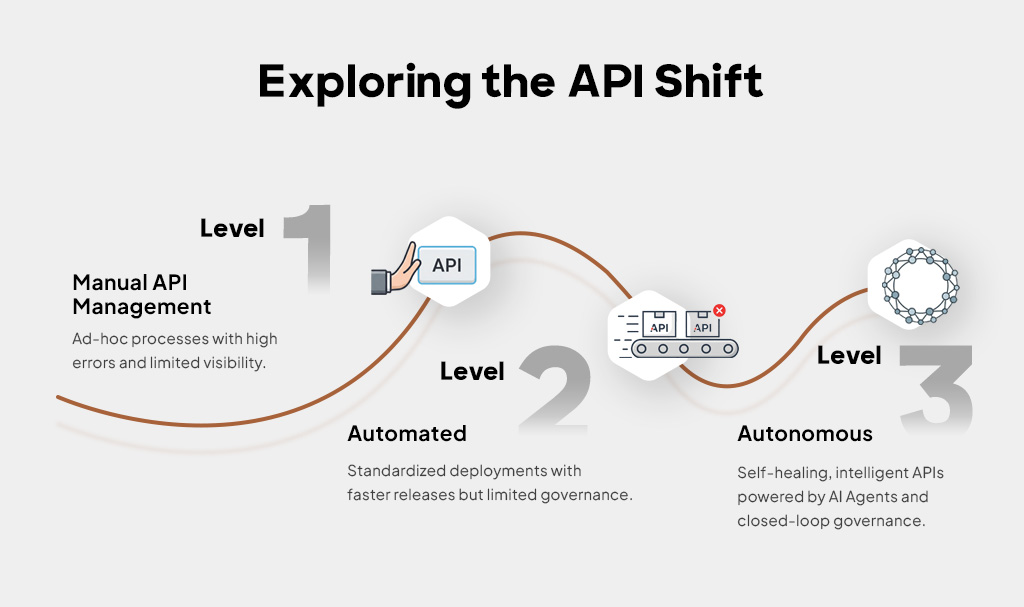
[Source]
The shift from manual to autonomous API management has been one of the most significant transformations in enterprise technology operations. For business leaders evaluating their API management strategy, understanding this evolution is crucial for making secure, informed decisions.
Phase 1: Manual API Management
In the early days of enterprise APIs, organizations relied heavily on manual processes that resembled traditional IT operations. Manual vs. automated API deployment was not even a consideration, as everything was handled by the dev teams.
Characteristics: Teams tracked API inventories in spreadsheets, managed access through email-based approval workflows, and deployed changes through ticket-driven processes.
Business Impact: This manual approach created significant business challenges.
- Release cycles stretched for weeks.
- Error rates remained high.
- Visibility into API performance was limited to reactive monitoring.
Most critically for executives, manual API management created a strategic bottleneck. The business agility was constrained by the speed of manual processes. Even the security model relied heavily on perimeter defenses, with teams addressing threats after they occurred rather than preventing them proactively.
Executive Reality Check: This reactive approach directly translated into a competitive disadvantage, as organizations struggled to respond to market opportunities at digital speed.
Phase 2: Automated API Management
The shift from manual to autonomous API management began with the introduction of rule-based automation, fundamentally changing how organizations approach API lifecycle automation. This stage introduced APIOps (intelligent API workflows) tools and best practices that brought consistency and speed to API operations.
Characteristics: Organizations implementing API management automation during this phase typically used CI/CD pipelines to automate deployment processes, policy frameworks to ensure consistency across all environments, and contract testing to reduce integration failures. Swagger and Postman were among the most commonly used tools for automating API management.
Business Impact: The benefits of transitioning from manual to automated API management were substantial, including faster releases, reduced errors, and improved consistency.
Strategic Limitation: However, rule-based automation still required significant human intervention for incident response, policy adjustments, and performance optimization. While teams learned how to automate API management workflows effectively, the systems largely remained reactive rather than predictive. Business leaders found that while operational efficiency improved, true competitive agility remained elusive as these systems had to be programmed for each function explicitly.
Phase 3: Autonomous API Management
True autonomous API management, which is gaining traction today, represents a fundamental shift that goes far beyond rule-based automation. This phase embodies AI Agents that utilize AI and ML to create self-governing API ecosystems.
Characteristics: Unlike API automation, which executes predefined workflows, autonomous systems continuously discover new endpoints, apply baseline policies intelligently, and perform remediation actions without requiring human approval.
AI Agents monitor runtime traffic patterns, detect anomalies using machine learning analytics, and optimize performance proactively. This represents the culmination of traditional APIOps, evolving into self-healing, intelligent workflows.
Business Impact: Organizations can respond to market opportunities at machine speed, scale resources intelligently based on predicted demand patterns, and maintain security posture through continuous threat detection and autonomous remediation. Summarizing the benefits of autonomous API management:
- Operational: Reduced MTTR (mean time to resolution) from hours to minutes
- Financial: Intelligent cost optimization and resource allocation
- Competitive: Market responsiveness at machine speed
- Governance: Continuous compliance without human oversight lag
Why Should You Automate API Management?
Four critical business drivers are making APIOps and autonomous API lifecycle automation an immediate strategic imperative.
- Scale
When business leaders consider the benefits of moving from manual to autonomous API management, scale becomes the most compelling argument. As enterprise applications now connect to between 26 and 50 API endpoints each (representing a 400% increase from just five years ago), manual approaches have broken down.
- Speed
Machine-to-machine interactions now dominate API traffic, requiring decisions at runtime velocity where human intervention becomes a competitive liability. What is needed is an AI Agent that processes thousands of transactions per second and delivers real-time API responses to all devices in the ecosystem. Consequently, autonomous API management addresses this speed imperative by reducing reliance on human decision-making delays in time-critical processes.
- Cost
Manual vs. automated API management becomes a cost equation that heavily favors automation. The human resources required to manage API calls and consumption manually would exceed the cost savings from the AI Agents themselves. Consequently, cost control becomes a strategic capability.
Autonomous API management systems can optimize usage patterns, negotiate dynamic pricing with providers, and prevent cost overruns through intelligent quota management. This capability enables organizations to scale API initiatives without creating unsustainable operational costs.
- Risk Mitigation
Despite APIs driving over 60% of internet traffic, approximately 25% of API endpoints remain unknown or unmanaged across enterprise environments. This represents a significant security and compliance risk that manual processes cannot effectively address.
The vulnerabilities in unknown endpoints can expose customer data, financial information, and intellectual property. As a result, compliance failures become inevitable when organizations can’t inventory and govern their complete API landscape.
How to Transition from Manual API Management?
The transition from manual to autonomous API management necessitates strategic planning and phased implementation to minimize business disruption while maximizing competitive advantage. Here is a step-by-step API lifecycle automation process that you can follow:
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment (Months 0-3)
The foundation of any successful API lifecycle automation initiative begins with comprehensive discovery. Organizations must first understand their current API landscape before implementing APIOps best practices.
Phase 2: Automation Foundation (Months 4-6)
With discovery complete, organizations can begin implementing API management automation through systematic workflow transformation. This phase focuses on how to automate API management workflows while maintaining operational stability and business continuity.
This includes:
- Implementing CI/CD pipelines for API deployment
- Establishing policy-as-code frameworks
- Introducing APIOps tools for continuous integration and testing
Phase 3: Intelligence and Autonomy (Months 7-12+)
The transition to truly autonomous systems represents the most strategically valuable phase of the transformation. This stage emphasizes the implementation of autonomous API management best practices that create and enable self-governing API ecosystems.
AI Agents are integrated for real-time anomaly detection, predictive scaling, and automated remediation. They continuously monitor API performance, detect security threats, and optimize resource allocation without human intervention.
Things to Consider Before Transitioning to Autonomous API Management
Before building and integrating custom AI Agents to manage APIs autonomously, note the following implementation considerations:
→ Leadership Requirements: Successful API transformation requires executive sponsorship that extends beyond initial approval. It requires an organizational change that brings in cross-functional teams, having API product owners, platform engineers, security specialists, and FinOps experts.
→ Investment Strategy: Organizations should view this transformation as a competitive investment rather than an operational expense. The benefits of moving from manual to autonomous API management compound over time, with capabilities providing sustainable competitive advantages that justify the initial investment.
→ Risk Imperative: Autonomous API management should reduce risk rather than increase it. Supporting our claim, the majority of manual vs. autonomous API management comparisons consistently show that automated systems produce fewer errors, maintain a better security posture, and provide more consistent outcomes than manual processes.
The Path Forward
Organizations embarking on this transition, from manual to autonomous API management, should focus on building capabilities incrementally while aiming to achieve (or retain) operational excellence. They must approach it as a strategic transformation that positions them for long-term competitive success in increasingly digital markets.
The question for business leaders isn’t whether to begin this transformation, but how quickly they can navigate the journey to achieve autonomous capabilities before competitors gain advantages through superior API operations and market responsiveness.
If you are struggling to envision a timeline or ROI, consider consulting or collaborating with a professional service provider. With reliable API development and integration services, you can audit and gain a detailed understanding of your API workflows. If you already have this insight, go directly to an AI Agent development company that can tailor autonomous API systems for your operations.
Author bio
Amelia Swank is a seasoned Digital Marketing Specialist at SunTec India with over eight years of experience in the IT industry. She excels in SEO, PPC, and content marketing, and is proficient in Google Analytics, SEMrush, and HubSpot. She is a subject matter expert in Application Development, Software Engineering, AI/ML, QA Testing, Cloud Management, DevOps, and Staff Augmentation (Hire mobile app developers, hire WordPress developers, and hire full stack developers etc.). Amelia stays updated with industry trends and loves experimenting with new marketing techniques.
